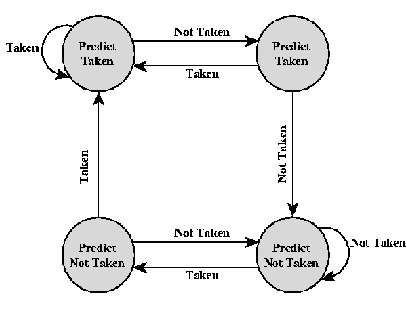
Il concerne les instructions de modification du registre PC. Le cas trivial est l'instruction de branchement conditionnel. Jusqu'à l'exécution d'une telle instruction, il est impossible de savoir si un branchement est effectué ou non. Par exemple, pour la machine RISC, l'adresse de l'instruction suivante n'est connue qu'au niveau de l'étage EX.
| cycle d'horloge | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| instruction 1 | LI | DI | EX | MEM | ER | |||
| instruction 2 | LI | DI | EX | MEM | ER | |||
| instruction 3 | LI | DI | EX | MEM | ER | |||
| instruction 4 | LI | DI | EX | |||||
| instruction 5 | LI | DI | ||||||
| instruction 6 | LI | |||||||
| instruction 7 | LI | DI | ||||||
| instruction 8 | LI |
! Cet aléa est le principal facteur de dégradation
de performance dans une architecture pipeline.
Plusieurs solutions ont été proposées pour gérer les branchements dans une architecture pipeline :
